Electrolysis machines are devices that take several electrolyzer stacks and connect them to a renewable energy source and water to create hydrogen.
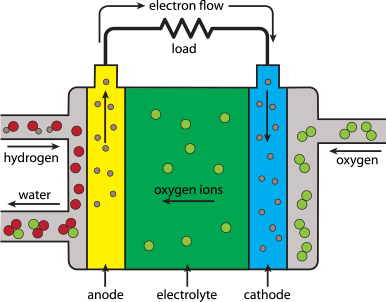
An electrolyser stack is the heart of the system that uses electricity to split water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) gases. This process is called electrolysis.
Every different type of machine has different heat loads, temperatures, and liquids, Thermogym understands the difference and can guide you through the process of development of the cooling systems of these machines.
For those that wish to underdstand more here is the explaination:
Why Split Water?
The sun doesn’t shine at night, and sometimes the wind doesn’t blow. Sometimes there is too much sun and wind, thus it is better in times of too much to drain off the excess energy into hydrogen for long term storage. Batteries are limited, but you can store an infinite amount of hydrogen in storage tanks.
Hydrogen produced by electrolysis is very clean and can be used as a fuel. It doesn’t produce harmful emissions when burned, just water. This makes it a good alternative to fossil fuels.
How Does an Electrolyser Work?
- Water Input: Water is supplied to the electrolyser.
- Electricity Input: Electricity is applied to the device.
- Splitting Water: The electricity splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- Gas Output: Hydrogen and oxygen gases are collected and can be used for various purposes.
Types of Electrolysers
There are three main types of electrolysers, each working a bit differently but achieving the same goal:
- Alkaline Electrolysers
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysers
- Solid Oxide Electrolysers
Thermogym has experts in all types.
Some say: “why waste water?” The truth is, the quantity of water required for mining and refining the same energy amount of the hydrogen is about 50 times the water use of direct conversion, with no pollution downstream!
Just ask and our experts will answer all of your questions.
Back to Energy solutions
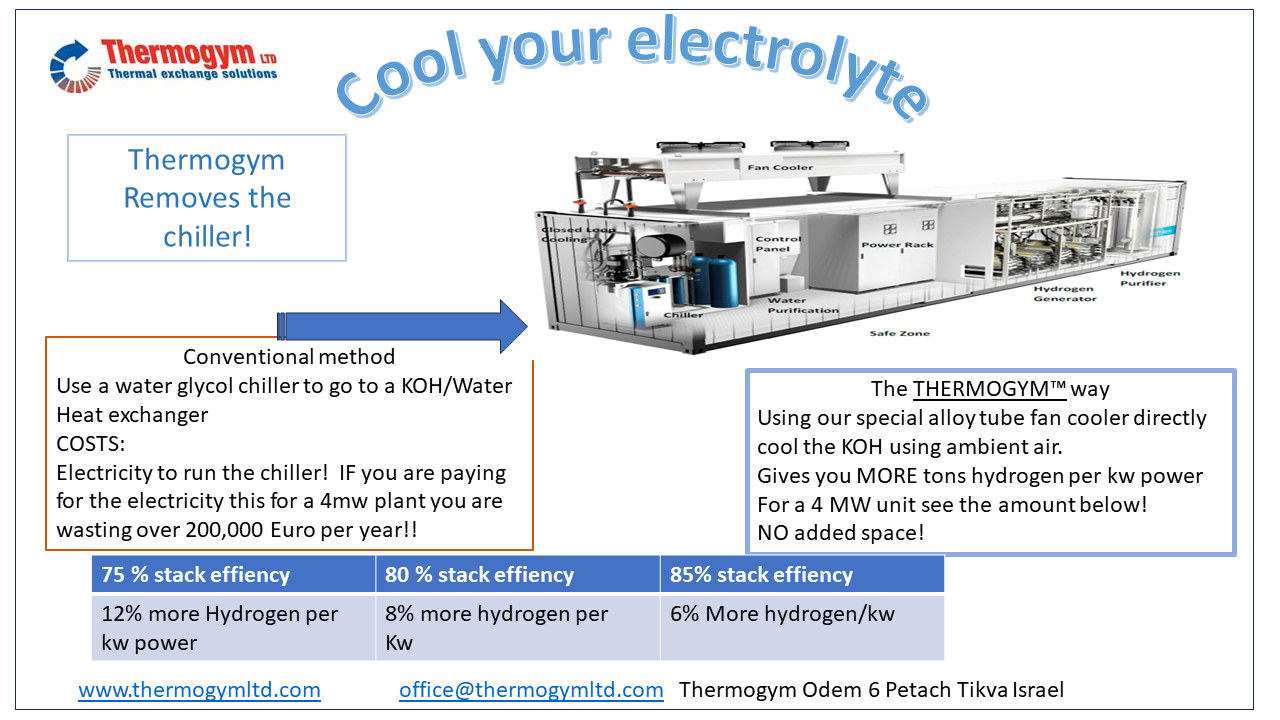
Alkaline Electrolyser
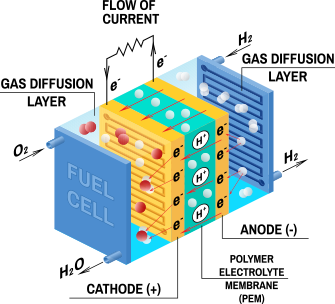
PEM Electrolyser cooling