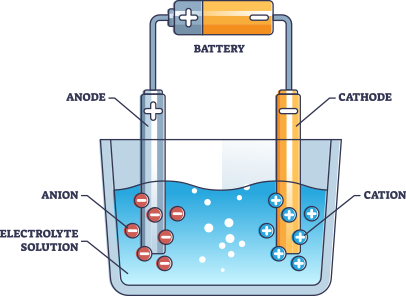
How They Work:
Electrolyte: Uses a liquid alkaline solution (usually potassium hydroxide, KOH, or sodium hydroxide, NaOH) to conduct electricity.
Electrodes: Two electrodes (anode and cathode) are placed in the alkaline solution.
Reaction: When electricity is applied, water molecules split into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Pros:
-
- Mature technology with a long track record
- Relatively low cost
Cons:
- Lower efficiency compared to PEM electrolysers
- Slower response to changes in electricity input
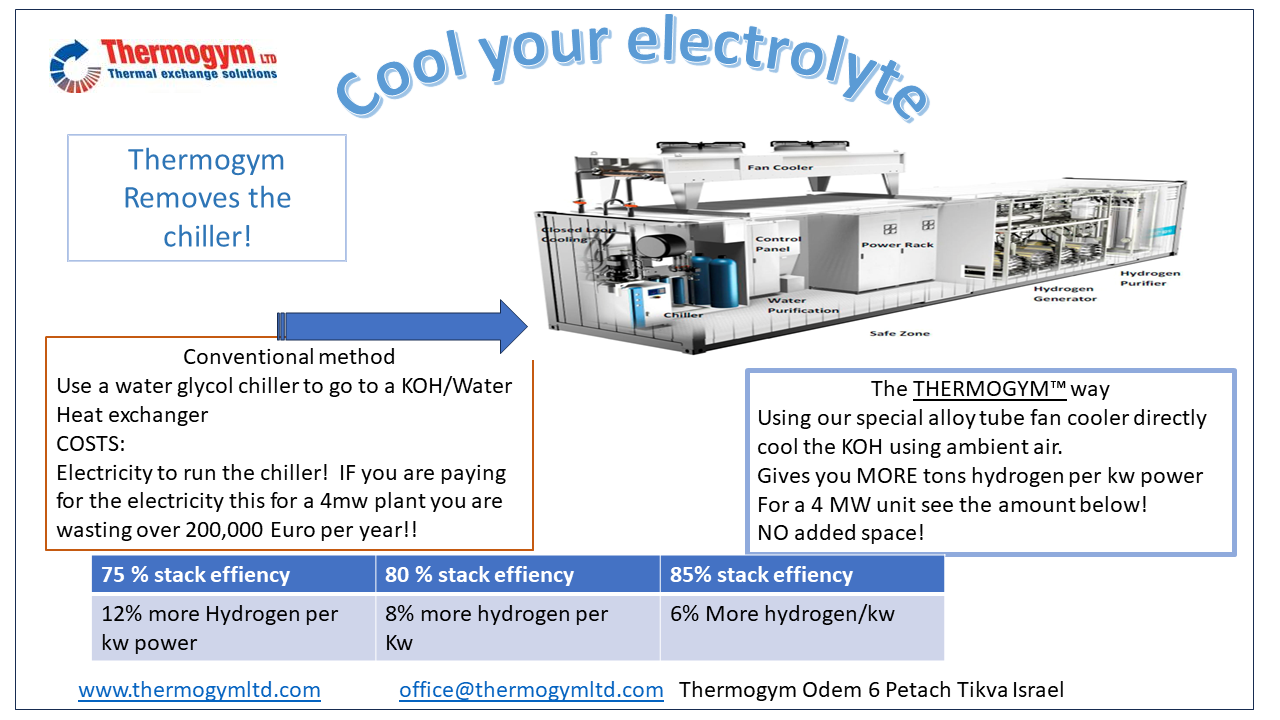
What is the problem with cooling these?
Due to the very reactive and corrosive liquids it is required to use a double system. There is a special liquid/liquid heat exchanger to cool the electrolyte. Then the cold water goes into a chiller loop, using refrigerant and a full cooling cycle. Then on the roof is a big condenser to remove the heat from the chiller. With Thermogym technology it is possible to DIRECTLY cool the electrolyte in the heat exchanger on the roof. This increases the kw out/kw in, as well as reduces the initial capital (capex) cost of the unit. For maintenance this is also great at reducing the complexity of the system.
No related products or energy posts found.

